Enable JavaScript Android phone – unlocking a world of interactive web experiences on your mobile device. Imagine seamlessly navigating dynamic websites, engaging with interactive maps, and effortlessly using web applications designed for a smoother, more responsive experience. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of JavaScript on Android phones, providing a clear path to unlocking the full potential of your mobile browsing.
From understanding the fundamentals of JavaScript execution on Android to practical steps for enabling JavaScript in different Android browsers, this guide covers every aspect. We’ll also explore how JavaScript powers various app types, highlighting the pros and cons of using it in web apps and hybrid apps. Security considerations and performance optimization techniques are also addressed, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the digital landscape.
Understanding JavaScript on Android Phones

JavaScript, a ubiquitous language for web development, finds its way onto Android phones through a fascinating interplay of technologies. It’s not directly executed by the phone’s operating system but rather by a specialized engine. This allows for dynamic web pages and interactive experiences on the mobile platform.JavaScript’s role on Android, like its desktop counterpart, is crucial for enhancing user experience and enabling rich interactivity on web pages.
However, there are significant differences in implementation and performance considerations compared to desktop environments. Understanding these nuances is essential for developers crafting engaging mobile web applications.
JavaScript Engines on Android
JavaScript engines, such as V8, are fundamental to the execution of JavaScript code on Android. These engines are highly optimized for speed and efficiency, allowing for smooth performance even on resource-constrained devices. V8, developed by Google, is particularly relevant to Android due to its integration within Chrome’s rendering engine, often the backbone of mobile web browsing.
JavaScript Environments on Android
Android browsers, often based on Chromium, utilize JavaScript engines for executing JavaScript code within the context of web pages. These environments differ significantly from desktop browsers in terms of available APIs and performance characteristics. Mobile devices have limited resources, and developers must consider this when crafting JavaScript code to ensure smooth performance.
Performance Considerations
Optimizing JavaScript performance on Android devices is critical for a positive user experience. Mobile browsers often face constraints related to processing power, memory, and network bandwidth. Developers should employ techniques such as code minification, careful use of APIs, and avoidance of resource-intensive operations to ensure responsiveness.
Limitations and Constraints
Running JavaScript on Android presents certain limitations compared to desktop environments. Resource constraints, such as limited memory and processing power, may affect performance. Developers must be mindful of these limitations and write efficient code that handles these factors. Network connectivity is also a crucial factor in performance. Mobile networks can fluctuate, and developers need to consider how to handle network interruptions to maintain application responsiveness.
Differences from Desktop Browsers
Key differences exist between desktop and Android browsers regarding JavaScript environments. Android browsers often prioritize battery life and resource management, impacting the execution speed of JavaScript code. Furthermore, the APIs available to JavaScript code might differ, leading to code adjustments for a seamless transition to mobile platforms. This difference requires careful attention to mobile-specific optimizations to prevent performance issues.
Enabling JavaScript in Android Web Browsers
Unlocking the full potential of the web on your Android phone often hinges on enabling JavaScript. This essential scripting language powers interactive elements, dynamic content, and countless web applications. Understanding how to enable JavaScript ensures a smoother, more engaging web browsing experience.JavaScript, a fundamental part of modern web development, enhances user experience by adding interactivity and dynamic elements to websites.
Without it, many sites might display static content or behave erratically. This guide will walk you through the process of enabling JavaScript in common Android web browsers.
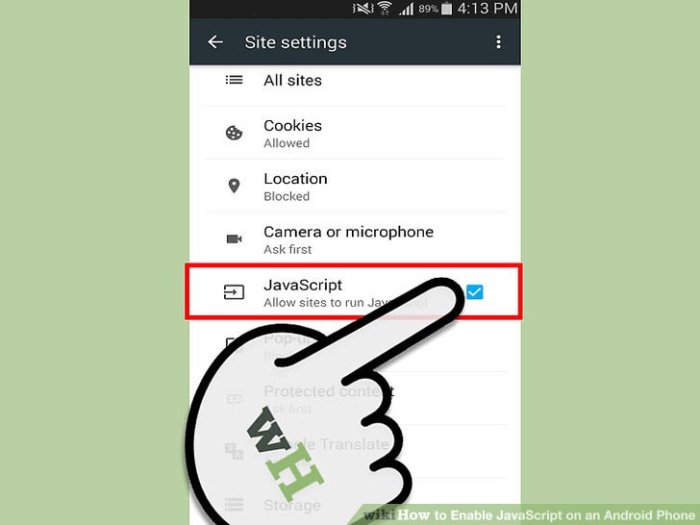
Enabling JavaScript in Chrome
To enable JavaScript in Chrome, navigate to the settings. Look for the “Site settings” or a similar option. Within the site settings, locate the JavaScript option. If you find it, select it, and then choose “Allow” or a similar confirmation. If this option is not immediately apparent, there may be a specific section for “JavaScript” or “Content settings.”
Enabling JavaScript in Firefox
Enabling JavaScript in Firefox involves accessing the browser’s settings. Locate the “Permissions” or “Content settings” section. From there, identify the JavaScript option. Once found, enable JavaScript by selecting “Allow” or a similar permission. This ensures interactive webpages function correctly within the browser.
Enabling JavaScript in Samsung Internet
Samsung Internet’s JavaScript settings are accessible through its settings menu. Find the “Content settings” or a comparable option. Within this section, locate the JavaScript entry. Select the “Allow” or “Enable” option to activate JavaScript in Samsung Internet. This is usually found within the permissions or content settings section.
JavaScript Enabling Methods Comparison, Enable javascript android phone
| Browser | Enabling JavaScript Method |
|---|---|
| Chrome | Navigate to Site settings, locate JavaScript option, and select “Allow.” |
| Firefox | Access Permissions or Content settings, identify JavaScript, and select “Allow.” |
| Samsung Internet | Find Content settings, locate JavaScript, and select “Allow” or “Enable.” |
Troubleshooting JavaScript Enabling Issues
If you encounter problems enabling JavaScript, try the following:
- Restart your browser: A simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches.
- Check for conflicting extensions: Extensions can sometimes interfere with JavaScript functionality. Disable or remove any recently added extensions to see if this resolves the issue.
- Clear browser cache and data: Sometimes, cached data can cause problems. Clearing your browser’s cache and data can help resolve any issues.
- Contact the browser’s support: If the issue persists, contact the support team for assistance. They can provide tailored solutions to resolve the problem.
JavaScript Applications on Android Phones
Android phones, with their powerful processors and vast ecosystem, are fertile ground for JavaScript applications. These applications, ranging from simple web views to complex hybrid experiences, play a significant role in the mobile landscape. From interactive games to sophisticated business tools, JavaScript’s versatility shines through on Android devices.JavaScript’s role extends beyond web browsing. It’s a key player in building dynamic and responsive user interfaces, allowing developers to create engaging and intuitive applications.
The language’s adaptability across various platforms, including Android, is a major reason for its popularity.
Different Types of JavaScript Applications
Various types of JavaScript applications thrive on Android. Web apps, accessed through a web browser, leverage JavaScript for interactivity. Hybrid apps, combining native code with web technologies like JavaScript, offer a blend of performance and flexibility. Native Android applications can even incorporate JavaScript frameworks for specific functionalities, broadening the possibilities.
Building User Interfaces with JavaScript
JavaScript empowers developers to create visually rich and user-friendly interfaces for Android applications. Libraries like React Native and Ionic facilitate the creation of interactive elements, allowing for dynamic updates and seamless user experiences. This approach makes applications feel native, minimizing the jarring transition between different parts of the application.
Comparing Web Apps and Hybrid Apps
Web apps, running directly in a browser, often have a lighter footprint. They leverage the browser’s rendering engine for display, providing a potentially more streamlined approach. However, web apps may face limitations in accessing native Android functionalities. Hybrid apps, on the other hand, offer a more seamless integration with native features, though they can be more complex to develop.
Table: Pros and Cons of Using JavaScript in Different App Types
| App Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Web App | Generally easier to develop, potential for quicker deployment, often more cost-effective for simple apps. | Limited access to native features, potential performance issues in complex scenarios, potentially less secure if not properly secured. |
| Hybrid App | Access to native features, generally good performance, good for apps needing platform features like location services, and offer a good balance of features and ease of development. | Development can be more complex, more development time and resources, and more difficult to debug. |
JavaScript Interaction with Native Android Components
JavaScript, in applications like hybrid apps, needs to communicate effectively with the underlying native Android components. This interaction is often facilitated through APIs that allow JavaScript code to call native Android methods and vice versa. This seamless communication enables access to device features, like the camera or storage, extending the application’s functionality. For instance, an application could use JavaScript to handle user input and then use native code to interact with the camera hardware.
Security Considerations with JavaScript on Android: Enable Javascript Android Phone
Unlocking the power of the web on your Android device is fantastic, but with that power comes responsibility. JavaScript, while crucial for interactive web experiences, can introduce security vulnerabilities if not handled carefully. Understanding these risks and implementing protective measures is paramount to ensuring a safe and enjoyable online experience on your Android phone.Protecting your Android device from malicious JavaScript code is like having a vigilant security guard at the digital gate.
Knowing the potential threats and how to defend against them is key to maintaining a secure online environment. This involves understanding the common vulnerabilities, implementing secure coding practices, and recognizing how to spot and prevent attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS).
JavaScript Security Risks on Android
Malicious JavaScript code can exploit vulnerabilities in Android web browsers to steal sensitive data, install malware, or redirect users to fraudulent websites. These risks are inherent in any system that allows for the execution of external code. Understanding these risks is crucial to developing a defense strategy.
Mitigating Malicious JavaScript Code
Several methods exist to reduce the risk of malicious JavaScript code exploiting vulnerabilities in Android web browsers. Robust security measures are crucial for a secure online environment. Implementing a layered approach, combining multiple strategies, is often the most effective method.
Common JavaScript Security Vulnerabilities
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a common vulnerability. Attackers can inject malicious scripts into legitimate web pages, allowing them to steal cookies, hijack user sessions, or redirect users to malicious websites. Other vulnerabilities include insecure direct object references and insufficient transport layer protection. These vulnerabilities can allow attackers to access or manipulate data in unauthorized ways. It’s essential to understand these weaknesses to protect yourself.
Secure Coding Practices for JavaScript on Android
Secure coding practices are essential when developing JavaScript for Android. This includes input validation to prevent malicious code injection, proper use of secure storage mechanisms, and regular security audits to identify and fix potential vulnerabilities. Adhering to secure coding practices is critical to building secure and trustworthy applications.
Identifying and Preventing Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks are a significant concern. By validating all user inputs, properly encoding output, and using HTTP only cookies, you can significantly reduce the risk of XSS attacks. Implementing these preventive measures is essential for creating secure web applications on Android. A robust defense against XSS is critical to maintain the integrity of the user experience.
Performance Optimization for JavaScript on Android
JavaScript, a cornerstone of the web, thrives on Android phones. Optimizing its performance is crucial for a smooth user experience. A well-optimized JavaScript engine translates to faster loading times, responsive interfaces, and a more enjoyable browsing experience. This involves various strategies, from code efficiency to asset management.Understanding the underlying mechanics of JavaScript execution on Android is vital for optimizing its performance.
Android’s unique architecture and resource constraints necessitate careful consideration. This is especially true when dealing with complex JavaScript applications or heavy web pages. A well-structured approach to optimization ensures the best possible user experience.
Techniques for Optimizing JavaScript Performance
Various techniques are employed to boost JavaScript performance on Android. These strategies aim to reduce loading times and enhance the responsiveness of user interfaces. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific needs of the application.
- Minification and Compression: Reducing the size of JavaScript files directly impacts loading times. Minification removes unnecessary characters like whitespace and comments, while compression algorithms shrink the files further. This significantly improves download speeds and reduces the load on the device.
- Code Splitting: Dividing large JavaScript files into smaller, modular chunks can dramatically enhance loading performance. Critical code is loaded initially, while less crucial components are loaded on demand. This approach reduces the initial load time and ensures a faster initial response. A real-world example includes loading the core features of a web app first, followed by additional functionalities as needed.
- Lazy Loading: Implementing lazy loading for images and other assets associated with JavaScript components avoids loading unnecessary data. This is particularly useful for complex web pages. A common use case is displaying images only when they are visible within the viewport, ensuring immediate responsiveness.
- Caching and Preloading: Leveraging caching mechanisms stores frequently accessed JavaScript files on the device. This reduces the need to download the same files repeatedly, resulting in quicker subsequent loads. Preloading essential components, especially those critical to application startup, can minimize perceived latency.
Improving Responsiveness of JavaScript-Driven User Interfaces
The responsiveness of JavaScript-driven user interfaces is critical for user satisfaction. Efficient handling of user interactions and asynchronous operations is crucial.
- Asynchronous Operations: Employing asynchronous programming techniques can prevent blocking the main thread during tasks like network requests or complex calculations. This ensures the application remains responsive and avoids a sluggish user experience. A simple example includes fetching data from an API without halting the interface’s responsiveness.
- Efficient Event Handling: Careful handling of user events ensures smooth interactions. Minimizing the complexity of event listeners and optimizing their execution sequence is essential. Complex event handlers can lead to poor performance. This can be mitigated by using a well-structured event handling system.
- Optimized DOM Manipulation: Reducing the frequency of DOM manipulations and using efficient techniques like document fragments can significantly improve responsiveness. Minimizing direct DOM manipulations and using document fragments can lead to improved responsiveness and a better user experience.
Using Efficient JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks
The choice of JavaScript libraries and frameworks directly impacts performance.
- Choosing the Right Libraries: Selecting libraries and frameworks tailored to the specific needs of the application is crucial. Optimizing libraries and frameworks for mobile environments is crucial to achieve the desired performance on Android devices. This includes exploring lightweight options, optimizing for Android-specific features, and understanding the trade-offs between functionality and performance.
- Framework Optimization: Frameworks like React Native can offer performance advantages by compiling to native code, leading to better efficiency on Android. A well-optimized framework, such as React Native, translates to a faster and smoother experience on Android devices. Understanding framework capabilities and limitations is crucial for optimizing performance.
Using JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks on Android
JavaScript, a language often associated with web development, has surprisingly powerful applications on Android. Leveraging robust JavaScript libraries and frameworks can significantly streamline the development process and unlock advanced functionalities. This approach allows for rapid prototyping and intricate UI/UX design, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with Android apps.JavaScript frameworks like React and Angular provide a structured approach to building complex user interfaces, offering reusable components and a well-defined architecture.
This modularity not only speeds up development but also fosters maintainability and scalability in the long run. These frameworks significantly reduce the amount of code required for common tasks, allowing developers to focus on the unique features of their app.
Popular JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks
JavaScript libraries and frameworks provide a structured approach to developing applications. Popular choices for Android include React Native, a framework that allows developers to build native Android apps using JavaScript. Angular, another popular choice, facilitates the development of complex applications with its component-based architecture.
Enhancements to Android App Development
These libraries and frameworks significantly enhance Android app development by providing pre-built components and tools, reducing development time and effort. React Native, for instance, empowers developers to leverage the familiarity of JavaScript while creating native Android applications. This familiarity is a key benefit, as it allows developers to quickly transition between projects and reuse their existing JavaScript skills. Angular’s component-based architecture allows developers to create modular, maintainable, and scalable applications.
Integration Process
The integration process for these libraries often involves setting up a development environment, installing necessary packages, and linking the framework to the Android project. Specific steps may vary based on the chosen framework and the project’s structure. Thorough documentation for each framework provides a clear roadmap for seamless integration.
Performance Implications
The performance implications of using different JavaScript frameworks on Android devices are a critical consideration. React Native, for instance, leverages native components to improve performance, resulting in a smooth user experience. This is crucial for maintaining responsiveness and avoiding lag in Android applications. However, performance can sometimes be influenced by the complexity of the application and the specific implementation.
Optimization techniques and careful consideration of the chosen framework’s architecture can mitigate these potential issues.
Practical Applications
These frameworks find applications in various domains. A social media application might benefit from React Native’s flexibility to rapidly build and update the UI, while an e-commerce platform could leverage Angular’s component-based architecture to create a complex, user-friendly interface. The use cases are wide-ranging, encompassing everything from interactive games to complex business applications. For example, a productivity app could employ React Native to quickly develop and deploy updates to enhance the user experience.
The choice depends on the project’s specific requirements.
