Dealing with attributable to: android.view.inflateexception: binary xml file line? This complete information dives into the center of this widespread Android improvement headache. We’ll dissect the error, discover troubleshooting methods, and equip you with the data to beat XML format points, useful resource conflicts, and extra. Prepare to remodel irritating errors into triumphant app improvement.
This detailed information unpacks the intricacies of the InflateException, tracing its roots to widespread XML format issues. From figuring out the offender line to mastering view inflation, we’ll present sensible options and examples to resolve this concern, guaranteeing your apps run easily and flawlessly.
Understanding the Error
The dreaded “android.view.InflateException: Binary XML file line…” error typically throws Android builders right into a debugging frenzy. This exception, a typical pitfall in app improvement, stems from points with how your app’s format is processed. Understanding its causes and signs is essential for efficient troubleshooting.This error alerts an issue in parsing the XML file that defines your app’s person interface.
Basically, Android’s format inflater encounters an issue whereas changing the XML description into the precise UI components. This normally means there is a battle, a lacking element, or an invalid attribute inside the XML format. The error message typically factors to a selected line quantity within the XML, offering a direct clue for locating the supply of the issue.
Causes of the InflateException
The “InflateException” arises from numerous issues in your format XML recordsdata. It isn’t all the time a easy mistake, however moderately a mixture of things. Cautious examination of the XML construction is vital.
- Incorrect XML syntax:
- Lacking or incorrectly formatted tags. It is a widespread rookie error. Making certain correct nesting of tags and attribute values is essential. For example, an unclosed tag or an attribute with a typo can set off this error.
- Incorrect attribute values:
- Incorrect attribute names or values. Misspellings or improper formatting of attributes inside the XML format may cause the error. Double-check all attribute values and names to make sure they’re right and match the anticipated format.
- Unresolved dependencies:
- Dependencies on exterior libraries or assets that aren’t accurately included or linked in your undertaking. Guarantee all exterior assets and libraries are accurately referenced in your undertaking.
- Useful resource Conflicts:
- A number of definitions of the identical useful resource, like layouts or kinds. This confusion in definitions can result in this error. Confirm there aren’t duplicate useful resource names in your undertaking’s useful resource recordsdata.
Frequent Eventualities and Examples
These eventualities are essential for understanding how the error manifests in numerous conditions.
- Lacking or Incorrect Views:
- Should you’re utilizing a customized view, guarantee it is accurately declared in your XML format file and that the category title is correct. A easy typo within the class title can result in this error. A typical instance: ` ` Make sure the `TextView` is accurately outlined and exists in your undertaking.
- Incorrect View Attributes:
- Incorrect use of attributes in views, like `android:layout_width` or `android:layout_height`. If these attributes are set to invalid values, the inflater will fail. An instance of a typical drawback: ` ` or an attribute worth that is not supported by the view.
- Nested View Errors:
- Issues with nested layouts. Be certain that the inside layouts are accurately nested and that there aren’t any overlaps or points in how the kid views are organized.
Error Traits
This desk supplies a structured overview of the “InflateException” and its widespread causes.
| Error Sort | Potential Causes | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| android.view.InflateException | Incorrect XML syntax, incorrect attribute values, unresolved dependencies, useful resource conflicts, lacking views, incorrect view attributes, nested view errors. | Confirm XML syntax, validate attribute values, guarantee dependencies are accurately included, examine for duplicate useful resource names, guarantee view courses are accurately outlined, double-check view attributes, examine nested layouts for points. |
Troubleshooting Methods
This information supplies a sensible strategy to tackling the “android.view.InflateException” error, particularly specializing in pinpointing the problematic line in your XML format recordsdata and using efficient debugging strategies. It is essential to grasp that environment friendly troubleshooting typically includes methodical examination and an excellent understanding of Android’s format construction. A well-structured and error-free XML file is crucial for a clean person expertise.Understanding the basis explanation for this exception typically includes systematically inspecting your XML file for inconsistencies.
This course of permits you to rapidly isolate the supply of the issue and effectively apply applicable fixes. Thorough debugging is vital to stopping utility crashes and guaranteeing a secure and responsive person interface.
Figuring out the Particular Line Quantity
Precisely figuring out the problematic line inside the XML file is essential for efficient troubleshooting. Android’s construct system supplies detailed error messages that usually embrace the offending line quantity. Rigorously look at these messages; they’re your major information. The stack hint, a significant element of the error message, will clearly level you to the problematic line quantity. It is a step-by-step breakdown of the sequence of occasions that led to the exception, enabling you to pinpoint the precise location of the error.
Inspecting the Related XML Code Snippet
As soon as you have recognized the road quantity, meticulously look at the corresponding XML code snippet. Search for potential errors in attributes, tags, or nested buildings. Frequent issues embrace typos, incorrect attribute values, or incompatible nested layouts. A radical examination will typically reveal lacking or further attributes, invalid XML syntax, or conflicting format parameters.
Systematically Checking XML Layouts for Points, Brought on by: android.view.inflateexception: binary xml file line
A scientific strategy to checking XML layouts for points is essential for stopping and resolving errors. Start by visually inspecting the format file for any apparent inconsistencies. Subsequent, confirm that every one tags and attributes are accurately fashioned and that the format construction is logical and well-organized. Rigorously examine the parent-child relationships between views to make sure compatibility and forestall conflicts.
This strategy will stop refined errors from escalating into bigger issues.
Evaluating Debugging Instruments for Android Growth
The next desk supplies a comparability of widespread debugging instruments, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in relation to dealing with this particular error.
| Debugging Software | Options | Use Instances |
|---|---|---|
| Android Studio Debugger | Step-by-step execution, variable inspection, breakpoints, and complete stack hint evaluation. | Figuring out the exact location of the exception, analyzing variable values, and stepping by way of the code. |
| Logcat | Shows system logs, offering worthwhile insights into utility conduct. | Monitoring utility occasions, figuring out potential points, and tracing the circulation of knowledge. |
| XML Editors (with validation capabilities) | Visible inspection of XML construction, real-time validation, and highlighting of potential errors. | Rapidly figuring out structural issues in XML layouts, checking attribute values, and guaranteeing correct formatting. |
XML Format Points: Precipitated By: Android.view.inflateexception: Binary Xml File Line
XML layouts are the spine of your Android app’s visible construction. A slight error in these layouts can result in irritating crashes or surprising conduct. Understanding widespread XML format points is essential for constructing strong and dependable Android functions. Let’s dive into the potential pitfalls and discover ways to navigate them successfully.Mismatched tags, attribute errors, and improper nesting in XML layouts may cause unpredictable outcomes.
Incorrectly formatted XML code can result in the dreaded `android.view.InflateException`. It is like a poorly constructed home; even a tiny flaw may cause main structural issues.
Potential XML Format Factor Points
A big supply of errors in XML layouts stems from incorrect use of XML components. Inconsistent or lacking closing tags, attribute errors, or improperly nested components are frequent culprits. Understanding these issues is vital to creating error-free layouts. Every aspect have to be structured accurately to make sure correct rendering and performance inside the Android framework. Mismatches, for instance, may cause the format engine to battle and fail, leading to an `InflateException`.
Mismatched Tags
Mismatched tags are a typical drawback in XML layouts. For example, opening a ` ` tag with no corresponding closing “ tag ends in an invalid format construction. This typically results in crashes or surprising rendering points. Making certain correct tag matching is prime to stopping these issues. Every opening tag requires a corresponding closing tag.
Attribute Errors
Attributes present essential data to format components. Incorrect or lacking attributes, or utilizing attributes with incorrect values, may cause points. For instance, specifying an invalid `android:layout_width` worth or omitting a required attribute like `android:id` can disrupt the format’s construction and performance.
Improper Nesting
Format components typically must be nested to attain the specified UI construction. Incorrect nesting can lead to unpredictable conduct and even crashes. The mother or father format must accommodate the kid format accurately. Nesting ought to be logical and align with the hierarchical construction of the person interface. A mother or father container ought to be able to holding the nested layouts inside its construction.
Frequent XML Format Syntax Errors
Errors in XML format syntax can manifest in numerous methods. Incorrect capitalization, lacking or further areas, and invalid attribute values can all trigger issues. Consistency in writing XML layouts is vital to avoiding these pitfalls. Adherence to Android’s XML format pointers is crucial.
Instance Desk of XML Format Errors
| Error | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Lacking Closing Tag | A tag is opened however not closed. | Guarantee each opening tag has a corresponding closing tag. |
| Incorrect Attribute Worth | An attribute has an invalid worth. | Confirm attribute values match the outlined sorts and ranges. Discuss with the Android documentation for legitimate values. |
| Incorrect Nesting | Format components are nested incorrectly. | Guarantee mother or father and little one layouts are suitable. Think about using a visible format editor to assist establish potential nesting issues. |
| Typo in Tag Identify | Incorrect capitalization or spelling of a tag. | Double-check the spelling and capitalization of all tags. |
Useful resource Conflicts
Useful resource conflicts are a typical offender behind the dreaded `android.view.InflateException`. Think about a home with conflicting blueprints – one requires a kitchen on the west aspect, whereas one other insists on it being east. This confusion results in a building catastrophe, very like the app crash you are experiencing. These conflicts typically come up from overlapping assets, like layouts, themes, or libraries.Understanding the supply of those clashes is essential for resolving them.
Useful resource conflicts happen when your app’s assets, like layouts or kinds, conflict with assets from libraries or different modules. Totally different variations of the identical library can have conflicting useful resource definitions, resulting in the `InflateException`. That is akin to making an attempt to suit two incompatible puzzle items collectively. You will have to establish the precise supply of the battle to repair the difficulty.
Figuring out Library Model Conflicts
Library model conflicts are a frequent supply of useful resource clashes. That is very true whenever you’re utilizing a number of libraries with overlapping assets. For instance, think about two libraries, every offering a customized `TextView` fashion, however with conflicting attribute values. One would possibly outline the `android:textColor` as `#FF0000`, whereas the opposite units it to `#00FF00`. Your app will don’t know which fashion to make use of, resulting in an error.
Instance Eventualities and Options
| Situation | Description | Potential Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Conflicting Types | Two libraries outline the identical fashion (e.g., `Theme.MyTheme`) with totally different attributes. | Guarantee compatibility between library variations or use a customized theme that overrides the conflicting attributes. |
| Duplicate Useful resource Names | Totally different libraries outline assets with the identical title (e.g., `format/activity_main.xml`). | Rename assets in one of many libraries, use totally different prefixes for library assets, or refactor your code to keep away from duplication. |
| Overlapping Library Dependencies | A number of libraries rely upon the identical library, however with totally different variations. | Rigorously handle dependencies utilizing Gradle’s dependency decision mechanism to keep away from model conflicts. Use a dependency administration software like Gradle. |
| Theme Conflicts | Two libraries outline themes with conflicting attribute values. | Prioritize the theme you propose to make use of in your app. You would possibly use a customized theme to resolve conflicting attributes. |
These examples spotlight how seemingly minor discrepancies in library variations or assets can create vital issues. Cautious dependency administration and useful resource decision are essential for stopping these conflicts and guaranteeing clean app operation.
View Inflation Logic
Android’s view inflation course of is sort of a refined recipe for constructing person interfaces. It takes XML descriptions of layouts and transforms them into tangible, interactive views on the display. This course of, essential for creating dynamic and responsive apps, can typically stumble if the components—your XML format—aren’t measured exactly. Understanding the mechanics of view inflation and the potential pitfalls in its logic is vital to avoiding the dreaded “android.view.InflateException.”The view inflation course of includes parsing the XML format file, instantiating corresponding views, and organising their relationships.
Errors on this course of can manifest in numerous methods, in the end resulting in the dreaded InflateException. One widespread supply of issues lies in how views are initialized or instantiated inside the format. Let’s dive into the specifics.
View Initialization Points
The way in which you initialize views in your XML layouts considerably impacts the inflation course of. Incorrect initialization may cause the inflation engine to fail, resulting in an InflateException. This failure usually stems from mismatched sorts or attributes within the XML or points with referencing assets.
- Useful resource Mismatches: A typical offender is a mismatch between the useful resource sort outlined within the XML and the precise sort of view you propose to create. For instance, making an attempt to inflate a Button with the format of a TextView will lead to an InflateException. The XML should precisely mirror the view sort.
- Lacking Attributes: Generally, essential attributes for a view are lacking from the XML. For example, if a TextView requires an “android:textual content” attribute, omitting it’s going to trigger inflation to fail. All essential attributes have to be current.
- Incorrect Attribute Values: Utilizing invalid or inappropriate values for attributes can result in issues. Setting an invalid colour worth or a dimension that does not make sense can halt the inflation course of. Legitimate values are essential for proper inflation.
Incorrect View Instantiation
The way in which you instantiate views, even when the XML is right, can nonetheless set off the InflateException. This typically occurs whenever you’re making an attempt to create customized views.
- Incorrect Constructor Utilization: A customized view might need a selected constructor with required arguments. If these arguments aren’t offered throughout instantiation, an InflateException will happen. Understanding the constructor parameters for customized views is crucial.
- Lacking Dependencies: In case your customized view depends on different libraries or assets, guarantee these can be found and accurately imported. Inflation can fail if important dependencies are lacking. The applying’s construct configuration ought to precisely mirror all essential libraries.
Instance of Incorrect View Initialization
Think about a format defining a customized view referred to as “MyCustomView”. The XML would possibly accurately reference the customized view, however the view’s constructor requires an integer parameter, which is lacking within the XML. This ends in a runtime InflateException as a result of the view can’t be correctly initialized.
<MyCustomView android:id="@+id/myCustomView" android:param1="10" />
The instance above illustrates the issue. If the customized view ‘MyCustomView’ has a constructor anticipating an integer parameter however the XML lacks this parameter, it causes the inflation error.
Dependency Administration Points
Challenge dependencies, just like the intricate gears of a well-oiled machine, are essential for a easily functioning Android utility. A hiccup on this delicate dance can result in surprising errors, and one widespread offender is a tangled internet of dependency conflicts. Understanding how these points come up is paramount to fixing them.
Issues with dependencies can manifest as a large number of errors, with the dreaded `android.view.InflateException` being a major instance. This exception, typically rooted in incompatibility points, signifies a failure to accurately inflate the format XML file. The basis trigger can stem from numerous sources, from outdated libraries to lacking packages, all in the end resulting in a irritating improvement expertise.
Outdated or Incompatible Dependencies
Dependencies, like software program elements, can turn into outdated or incompatible with the undertaking’s present construction. Think about making an attempt to suit a sq. peg right into a spherical gap; the end result will probably be a irritating mismatch. This incompatibility can manifest in surprising behaviors, errors, or crashes. For instance, an outdated model of a library may not be suitable with a more moderen model of Android’s SDK, inflicting the dreaded exception.
Equally, a library that depends on a selected API model would possibly fail to operate accurately with a special model.
Lacking Dependencies
A lacking dependency is akin to a lacking cog in a machine. With out it, the applying can not operate as meant. This ends in compile errors or runtime crashes. For example, if the applying requires a specific library for picture processing, but it surely’s not included, the applying will possible encounter errors when trying to make the most of that performance.
Dependency Conflicts
Conflicts come up when two or extra dependencies require conflicting variations of the identical library. Consider it like having two totally different units of instruments, every with their very own incompatible specs. This will result in unpredictable conduct, rendering the applying unusable. A library would possibly rely upon a selected model of a framework, and one other library would possibly require a special model, making a battle that’s exhausting to resolve with out cautious consideration.
Dependency Administration Software Comparability
| Software | Strategy to Conflicts |
|---|---|
| Gradle | Gradle’s dependency decision system makes an attempt to resolve conflicts by contemplating dependency declarations and their transitive dependencies. It supplies mechanisms for specifying variations and resolving conflicts, typically robotically. |
| Maven | Maven’s dependency administration system makes use of a central repository and coordinates dependencies based mostly on declared variations and their compatibility. It’s generally utilized in Java initiatives and supplies a strong mechanism for dependency administration. |
| Ivy | Ivy, one other common dependency administration software, focuses on dependency administration by way of a declarative strategy. It presents flexibility and fine-grained management over dependency decision. |
Choosing the proper dependency administration software can considerably influence the steadiness and maintainability of your Android undertaking. Understanding their approaches to battle decision permits builders to mitigate potential points and streamline the event course of.
Dealing with the Error in Code
InflateException – a irritating buddy for Android builders. It is a widespread error that usually leaves you scratching your head, questioning what went flawed in your meticulously crafted XML layouts. However worry not, intrepid developer! This part will equip you with the instruments to tame this troublesome exception.The core concern is that your app cannot inflate a format – it may’t learn and assemble the visible construction you have designed.
This normally factors to a mismatch or an issue inside the XML construction itself or the way in which your code tries to make use of it.
Utilizing Attempt-Catch Blocks
Dealing with InflateException gracefully is essential for a clean person expertise. A well-placed try-catch block can stop your app from crashing when an exception happens. The attempt block accommodates the code that may throw an exception, whereas the catch block handles the exception if it arises.“`javatry // Code that may throw an InflateException, resembling inflating a view View view = getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.format.my_layout, null); catch (InflateException e) // Deal with the exception Log.e(“InflateException”, “Error inflating view: ” + e.getMessage()); // Show a user-friendly message Toast.makeText(this, “An error occurred whereas loading the format.”, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).present(); // Think about exhibiting a default format or a loading indicator.“`This structured strategy ensures that your app continues operating even when an issue is encountered.
By logging the exception, you may higher diagnose the basis explanation for the difficulty sooner or later.
Logging and Person Suggestions
Logging the exception, as demonstrated above, supplies invaluable insights into the issue. Use the Log class to report the error particulars. It’s best to present the person with a useful message, moderately than leaving them with a cryptic error.A well-crafted message ought to inform the person of the issue with out overwhelming them with technical jargon. Think about displaying a easy Toast message or a extra detailed dialog, relying on the severity of the difficulty.
Finest Practices for Exception Dealing with
Strong exception dealing with is a cornerstone of constructing dependable Android functions. Listed here are some greatest practices:
- Particular Catch Blocks: Use particular catch blocks for InflateException, moderately than a generic Exception catch. This allows you to deal with the issue extra successfully and supplies extra informative error messages.
- Clear Error Messages: Craft clear and concise error messages for the person. Keep away from technical particulars except essential. Present a useful answer or steering.
- Logging: Log the exception with related particulars, such because the file title and line quantity the place the error occurred. This helps in debugging.
- Stopping Crashes: Deal with the exception gracefully to forestall the app from crashing. Present a fallback mechanism or a default view in case of an error.
Following these greatest practices helps create a extra resilient and user-friendly utility.
Frequent Error Eventualities

Navigating the complexities of Android improvement can typically result in irritating errors. One such widespread pitfall is the dreaded `android.view.InflateException`. This exception, typically stemming from points along with your XML format recordsdata, generally is a actual headache to troubleshoot. Let’s dive into some widespread eventualities and discover ways to keep away from them.Understanding the basis causes of `InflateException` is vital to fixing them successfully.
It is typically a symptom of issues inside your format’s construction, useful resource administration, or dependencies. The next sections Artikel widespread error eventualities, illustrating good and dangerous practices, that will help you create strong and error-free layouts.
Examples of Error-Susceptible XML Layouts
Incorrectly structured XML layouts are a frequent supply of `InflateException`. Understanding the refined methods XML can journey you up is essential for stopping these errors.
- Lacking or Incorrect Attributes: A typical mistake is forgetting important attributes, such because the `android:layout_width` or `android:layout_height` for a view. This ambiguity confuses the format engine, triggering the exception. For instance, in case you omit the width and peak attributes for a TextView, the format engine struggles to find out how a lot house to allocate.
- Useful resource Conflicts: Utilizing the identical useful resource title for a number of components may cause conflicts. The system would not know which useful resource to make use of. Think about a button and a textual content view each utilizing the identical ID. The format inflator struggles to differentiate them, leading to a conflict.
- Incorrect View Hierarchies: Misplacing or misnesting views in your XML format can create structural issues. For instance, making an attempt to position a `LinearLayout` inside a `RelativeLayout` with out applicable constraints will throw an error. The system would not perceive the association of views.
- Incorrect Dependency Administration: Lacking dependencies or conflicts between dependencies can even set off this exception. For example, if a library you are utilizing has a conflicting definition for a view, you would possibly run into issues. This might occur in case you’re not utilizing the right variations or kinds of libraries. Think about needing a selected model of a library to render a view, however your undertaking is utilizing an older model that does not assist the specified performance.
Properly-Structured XML Format Instance
This instance demonstrates a well-structured format that’s much less vulnerable to errors.“`xml “`
Poorly Structured XML Format Instance
This instance demonstrates a poorly structured format that may possible trigger `InflateException`.“`xml “`
Comparability Desk
This desk highlights the important thing variations between the well-structured and poorly structured layouts.
| Attribute | Properly-Structured Format | Poorly Structured Format |
|---|---|---|
android:layout_width |
Current for all views | Lacking for some views |
android:layout_height |
Current for all views | Lacking for some views |
| Useful resource Conflicts | No conflicting useful resource names | Probably conflicting useful resource names |
| View Hierarchy | Appropriate nesting of views | Incorrect nesting of views |
Troubleshooting Suggestions
Unveiling the mysteries of the dreaded `android.view.InflateException` requires a detective’s strategy. This error, typically lurking within the shadows of advanced XML layouts, can stump even probably the most seasoned Android builders. However worry not! With the correct instruments and strategies, you may pinpoint the supply of the issue and restore your utility to its former glory.
This part supplies a roadmap for systematically investigating and resolving `android.view.InflateException`. It dives deep into essential debugging methods, providing actionable steps to diagnose and resolve the difficulty, irrespective of the basis trigger.
Checking for Typos in XML
A seemingly insignificant typo in your XML format file can set off this exception. Double-checking each tag, attribute, and worth is essential. Rigorously scrutinize the XML format recordsdata, guaranteeing correct syntax and proper attribute values. Search for misspellings, incorrect IDs, and inconsistencies. An oz of prevention is value a pound of remedy with regards to meticulously checking XML recordsdata.
Utilizing a devoted XML editor or a code formatter can help in recognizing errors and inconsistencies. Such instruments may help establish discrepancies that could be ignored throughout guide inspection.
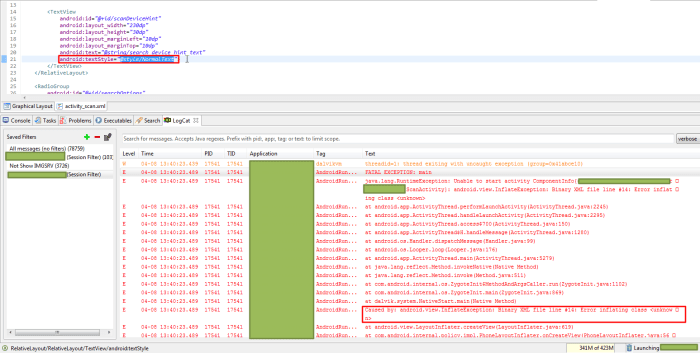
Inspecting Logcat Output
The logcat, your utility’s detailed occasion log, is a treasure trove of knowledge for troubleshooting. It typically supplies particular clues about the reason for the `InflateException`. Pay explicit consideration to the stack hint inside the logcat output. This hint typically factors to the exact line of XML code that triggered the error. A complete understanding of the stack hint might be invaluable in figuring out the basis trigger.
Analyzing the logcat output is like having an in depth dialog along with your utility, offering perception into the sequence of occasions that led to the exception.
Debugging Methods
Using efficient debugging strategies is crucial in swiftly resolving this concern. Thorough debugging includes a multifaceted strategy. The next strategies are instrumental in diagnosing and rectifying the error.
- Validate XML Construction: Use an XML validator to examine for any syntax errors. A well-structured XML file kinds the bedrock of correct format inflation.
- Examine Useful resource Recordsdata: Confirm that every one assets referenced within the XML format exist and have the right format. Be certain that the IDs and names in your XML format correspond to precise assets.
- Study View Inflation Logic: Rigorously look at the code liable for inflating the format. Search for any potential points, resembling incorrect parameter utilization or improper dealing with of exceptions.
- Isolate the Drawback: If doable, simplify the format by eradicating advanced components or elements. This may help to pinpoint the precise a part of the format inflicting the error. Begin with the best doable format and incrementally add complexity.
- Confirm Dependencies: Be certain that all essential libraries and dependencies are accurately built-in into your undertaking. Verify your construct configuration for any lacking or conflicting dependencies.
